I am here to tell you about the strongest muscle in the human body. The human skeleton is known as the internal skeleton because it supports the rest of the body. Many bone tissue and cartilage constitute this framework. While the ligaments and tendons are also found in close association with the components of the skeleton, the fibrous connective tissue may also be found.
This article focuses on the overall shape and function of the skeletal structure of the typical adult human. A human skeleton is composed of eight bones, four of which are paired or mismatched. The spine is made up of 33 different types of vertebrae. There are 14 bones in the facial skeleton; six are paired and two are unpaired. These bones make up the cranium (brain box). These are two separate components of the human body.
It also includes clavicles, a rib cage, and an extended pelvic bone called the scapulars. The metatarsals and phalanges make up the skeleton of the human foot. They are made up of five different parts, each with its unique structure. The bones of the feet are also known as the metacarpals and pectoralis major.
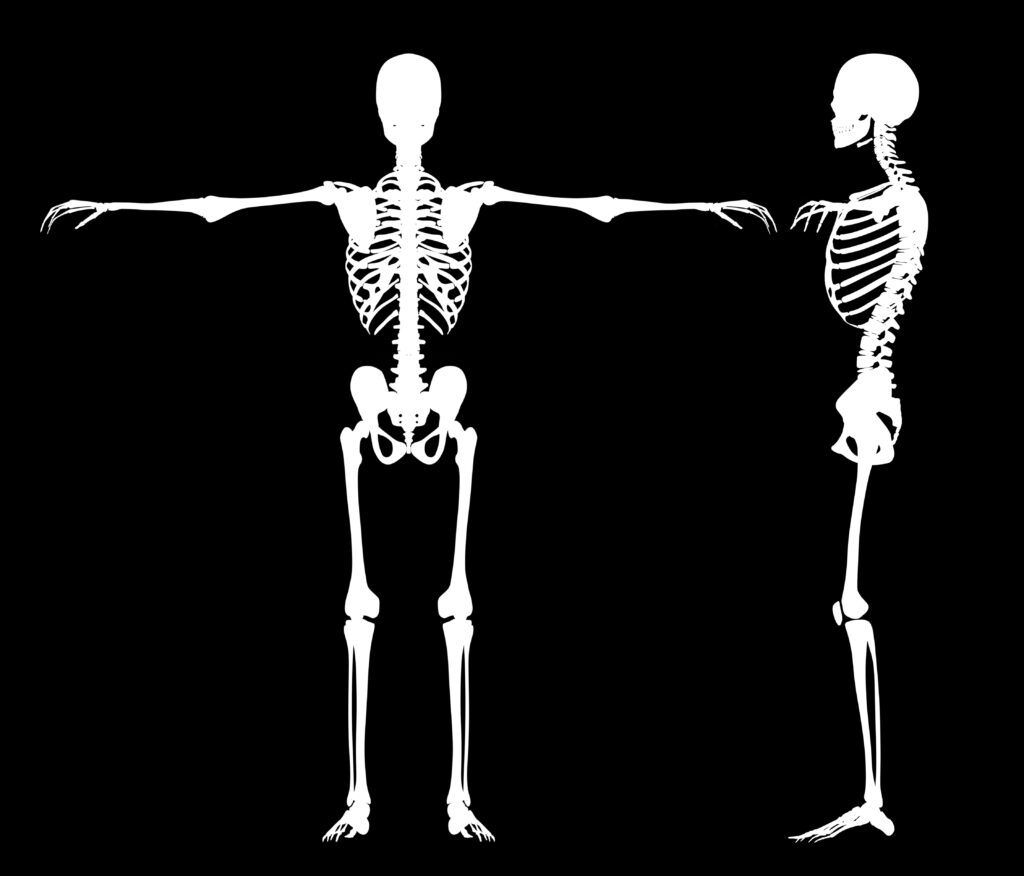
As the skeletal structure of a baby is far more fragile than that of an adult, an infant skeleton contains approximately 100 more bones than an adult skeleton. The process of bone development starts around the tightness in stomach during pregnancy third trimester. and continues throughout adulthood. The sacrum is an example of multiple bones that fuse over time to form one bone. As an embryo, the sacrum is comprised of five vertebrae with intervertebral discs between them. Sacral fusion typically occurs between the fourth and tenth decades of life.
What is the Strongest Muscle in the Human Body?
Table of Contents
The heaviest muscle, the masseter, is the strongest muscle in the human body due to its weight. By cooperating, all the muscles in the jaw are capable of exerting as much force as 55 banners in 27 countries (25 kilograms) on the incisors or as much as 200 pounds (90.7 kilograms) on the molars. You may be stronger overall, but you don’t have the strongest muscle in the human body in your knees, chest, hands, or back. Having a strong intellect may help you do anything, no matter how difficult
These are two separate components of the human skeleton.
1 Axial skeleton (transverse spinal column)
2 Appendicular skeleton (vertebral column)
1 Axial Skeleton (Symmetrical Skeletal Structure)
It is the body’s axis. The mentioned structures are included in this model.
Skull
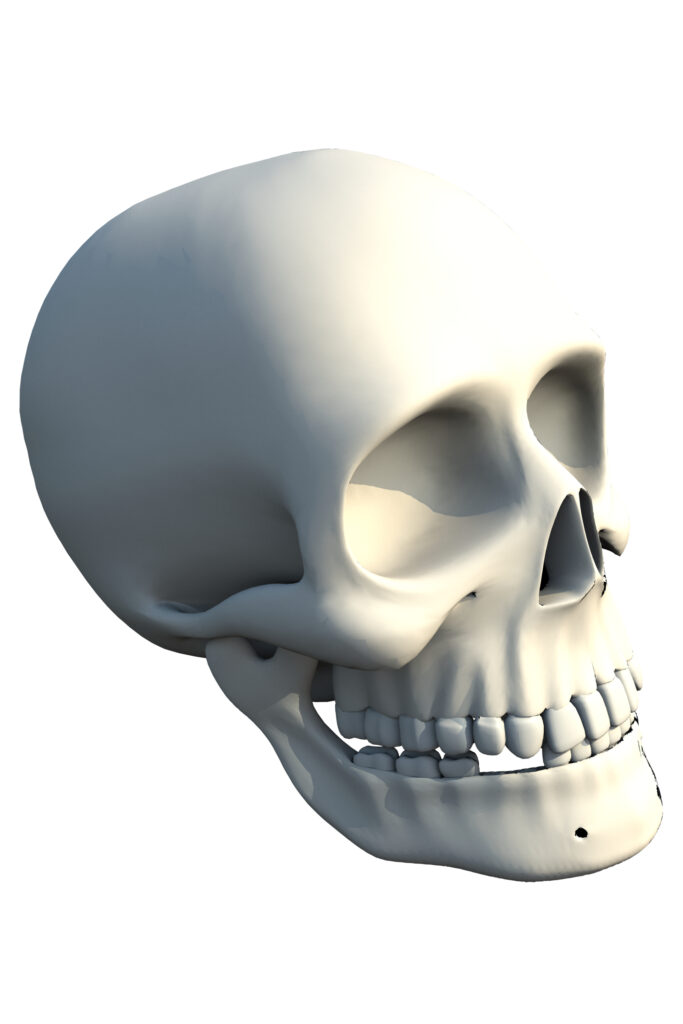
A human skeleton is composed of a mix of the skull and facial bones. The skull contains 22 bones, except for the jaw, which is separate. In children, the 21 fused bones are separated to let the brain and skull develop, but in an adult, they unite to provide strength and protection. The mandible is the only moveable joint in the skull and acts as a movable jaw bone. the skull is considered the strongest muscle in the human body.
Cranium (brain box)
It is one of the skulls’ outer surfaces. 8 bones make up the skull. The resulting four are unmatched, and the remaining two are coupled. It keeps the brain protected. Parietal bones are paired bones, while temporal bones are singly situated. Without a partner, the bones at the front of the head are the frontal bone, the occipital bone, the sphenoid bone, and the ethmoid bone.
Bone-in the face
There are 14 bones in the facial skeleton; six are paired and two are unpaired. Additionally, it is made up of paired or mismatched bones. Palatine, inferior concha, lacrimal, nasal, inferior maxilla, and inferior zygomatic are paired bones. Unpaired bones are also known as the mandible and vomer. A lower jaw with mandala bones and maxillae produces the upper jaw.
The spinal column (Vertebral Column)
The vertebral column runs from the head to the pelvis. It is a part of the backbone. It is specifically made to protect the spinal cord. because it is also considered the strongest muscle in the human body. On average, the vertebral column contains four curves, which increases its strength over a straight column. The individual vertebrae are made up of 33 of them.
Different Types of Vertebrae
Their names are given according to where they are found in the spinal column. Specifically, these vertebrae are known as vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, and pelvic vertebrae.
Vertebrae in the Neck
This is a group of seven, each found in the neck area. The Atlas vertebra is the first of the two cervical vertebrae.
Backbone Vertebrae
In the thoracic area, there are 12 vertebrae present.
Made from lumber
These are 5 in number present in the pelvic and thoracic regions.
Pelvic Vertebrae
9 pelvic structures are located here.
These two groups Constitute two Sets
- Serum
Anterior The 5 vertebrae fuse to create the cervical vertebrae.
- Coccyx
It is made up of the union of the 4th vertebrae and the posterior regions of the spinal column.
Rib Cage (Abdominal Cavity)
How many ribs are in the human body?
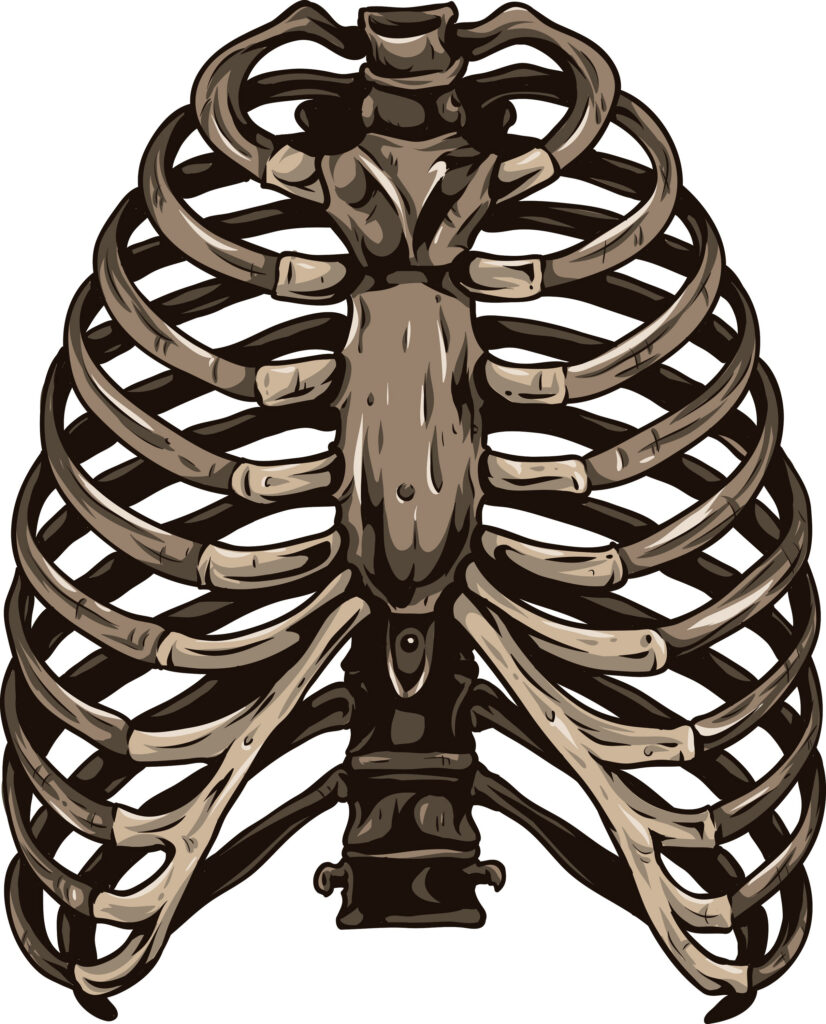
Each rib has 12 pairs, which are connected to the thoracic vertebrae through rib cartilage. Either directly or via the costal arch termed the genuine ribs, 10 pairs of the rib cage are linked anteriorly. Because they are not connected to the sternum, the bottom 2 sets of ribs are known as floating ribs True ribs are connected to the hip bone by carpal bones called costal cartilages, which are in turn joined to the sternum by the seventh and last pair of ribs.
The first three ribs have their southern coastal cartilages linked to the tissues above them, the false ribs. Ending in the abdomen is the way that the final two floating ribs’ cartilages finish. The rib cage is both semirigid and expansive, increasing in size due to the actions of many muscles. When air enters the lungs, the pressure in the lungs decreases below those of external air, which has to rush in to bring it back to balance. These activities are sources of inspiration (breathing in).
The relaxing of the heart muscle and the variable increases of the alveoli cause the air in the lungs to exhalate (breath out). Other ligaments and tendons connected to the bones of the thorax also help this process. The large muscle separating the chest and belly is the stomach, which originates from the ribs and the spinal column. The five lower ribs provide the chest room to expand and allow the diaphragm to move.
Function
Rib cage support is applied to a semi-vacuum chamber, often known as the chest cavity. It keeps the lungs and heart safe.
2 Appendicular Skeleton (Vertebral Column)
The appendicular skeleton comprises all of the following:
- The pecs and various appendages
- It comprises the pelvic girdle and the appendages
Girdle of the Pectoral
A wing-like skeletal girdle. The forelimb connects to the trunk area via the pectoral girdle. This one follows the other bones.
- Single scapula
- Above the scapula
- The 3rd clavicle
Clavicle
The shoulder is a relatively weak bone. The connection between the scapula and the sternum is made there. While the clavicle serves mostly as a guideline for scapular mobility, it does have a supporting role as well.
The limb on the Forepaw
In one forelimb you will find one of the upper arm humerus, the bottom two-arm radii and ulna bones, eight carpal bones, five metacarpals, and 14 phalanges.
Humerus
It is made of a single bone. It connects the scapula with a ball-and-socket joint. It creates a hinge connection between the radius and ulna at the distal end.
Radius and Ulna
The carpals (with eight wrist bones) are part of a multistage joint found distally on the hand.
Carpals
Eight numbers are listed here. Their hand becomes a wrist.
Metacarpals (acephalic)
Five metacarpals exist. The bones in the back of the hand provide the frame for the hand.
Phalanges
There are 14 of these fingers on each hand, and they are affixed to the metacarpals. The fingers are supported by these.
An Extended Pelvic Girdle
The pelvic girdle joins the archival purposes to the spinal column. Two coxal bones comprise it. The three vertebrae are fused to create a single bone known as the coxal bone. astrocytes, ischium, and pubis. The pelvic girdle helps support the pelvic area.
Hind limb (lower leg)
The hind limb consists of the following bones: the pelvis, ilium, ischium, and tibia.
Femur
It is also known as the proximal thigh bone. It connects at the hip joint with a ball-and-socket joint.
Tibia
The knee joint is located at the medial end of the femur, whereas the distal end of the femur is the end of the femur. Only the femur (thigh bone) is involved in the development of the knee joint. They create a junction between the tarsals and the distal end.
Tarsals
This is the eighth set of bones. Achy ankles are the result. These bones’ distal ends are connected to the five metatarsals.
Metatarsals
This is comprised of five items. Also known as the metacarpals, the distal ends of their limbs are joined by phalanges.
Phalanges
This is an arrangement of fourteen toes. Each toe is placed in a row with others of its kind. Foot phalanges are much sturdier than hand phalanges.
Joints
A joint is unusual since it’s made up of two separate bones. joints are loosely attached bones. It is the connective bone supporting tissue. Furthermore, they enable mobility Ligament is the bone supporting tissue. Joints protect the body because they are also considered the strongest muscle in the human body.
Based on the amount of mobility permitted, joints are divided into three groups.
- Immovable joints, including those in the skull, pelvis, and teeth, serve as examples of this concept.
- Adjoints that allow little movement symphysis pubis.
- The elbows, for example, have moving joints.
There are two kinds of freely moveable joints
- Intermediate joint
- Socketed connection
Structural Classification of Joints
Additionally, the joints are categorized according to their structure.
Very Elastic Joints
This is connected with connective tissue that is interwoven with short-fibered collagen fibers. Present in the skull is there. They treat dental issues in the jaw.
Joints Formed from Cartilage
There is very little or no mobility in these joints. developing bones come together to create a hyaline cartilage joint. Cartilage holds the bones together. Between the vertebrae at the site where the coxal bones connect in front of the pelvis, these things are present.
Joints with Synovial Lubrication
The fluid-filled cavities in these joints act as shock absorbers. The fluid in this jar is used to decrease friction between the mechanical parts. This joint is enveloped by a fibrous capsule of connective tissue. The synovial membrane, the outermost layer of synovial fluid, is the foundation of the inner layer. certain ligaments are formed using portions of the capsule as a starting point. The ligaments are responsible for maintaining the bones in place.
1 Hinge Joints
It enables two-way motions. Additionally, they’re also seen at the elbow and knee. In this way, two groups of muscles are positioned in an opposed configuration.
2 A Ball and Socket joint
These joints contain at least two muscle pairs present parallel to each other. These let you make the most of your options. Like the hip joint and the shoulder joint, the ball and socket bones serve as an example of these Strongest Muscle in the Human Body.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is the second strongest muscle in the human body?
It’s debatable which muscle in the body is the strongest. Some physiologists assert that it is the gluteus maximus, while others believe that it is the masseter (used for chewing).
What is the strongest muscle in the human body relative to its size?
The masseter, measured by weight, is the strongest muscle. Together, the muscles of the jaw may close the teeth with a force of up to 200 pounds (90.7 kilograms) on the molars and 55 pounds (25 kilograms) on the incisors.
Why is the tongue the strongest muscle in the human body?
The tongue is unquestionably not the body’s strongest muscle, though, that much is clear. Perhaps people still have faith in its power.
“medshelper.com, a health writing expert known around the world, was co-founded by Aneeza”
I want to be sure you get all the knowledge upgrades absolutely free since that’s what I’m speaking about.