The kidney is made up of nephrons, which perform all of the functional unit of the kidney. More than 20 million nephrons are present in each human kidney. Nephrons can be found in the outer cortex and the inner medulla. They also play a role in blood filtration. Bowman’s capsule surrounds a cluster of capillaries called glomerulus in each nephron.
The inner end has a cup-shaped swelling, termed Bowman’s capsule. Nephrons’ blood supply is circulated through the glomerular capillaries. . Your kidney helps rid your body of waste and excess fluid. Exercise regularly and stay fit. Do not do over exercising. Keep an eye on blood pressure. Don’t overeat, monitor weight. It is very unhealthy to smoke.
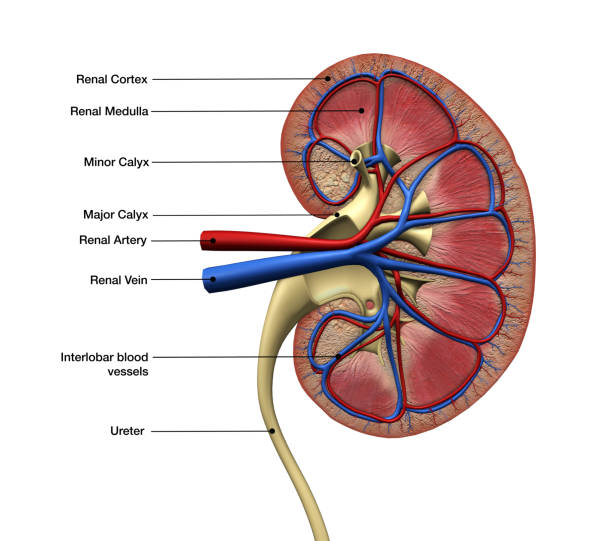
Two bean-shaped structures, called the kidney, are part of the renal tubule system. They assist the body in the excretion of waste using urine. They are also used in the process of blood filtration before delivering it directly to the heart. In addition to its numerous tasks, the kidney is also involved in many other critical processes, which include maintaining good water levels.
Where are the nephrons placed in the kidney’s structure? Every single functioning unit inside a kidney is known as a nephron. Because of the high blood supply of the nephrons, which exit each kidney via the renal vein, there is a continuous blood supply for the kidneys. In this section, we are going to discuss what is the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
What is the Functional Unit of the kidney?
Table of Contents
The functional unit of the kidney is the: nephron. It can be seen that renal blood’s primary role is waste clearance since kidney tissue weighs just around 1% of total body weight but receives 20% of blood given each time the heartbeats. To complete the filtering of blood and the subsequent processing via the tubular system, the main cavity of the renal and the pelvis are used. The ureter carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The functional unit of the kidney helps you a lot to live a happy life. which is the functional unit of a kidney.
The ureteral aperture is the opening through which both the ureters empty into the urine bladder. pee exits the body when you go to the bathroom, which happens during urination when the bladder releases its contents into the urethra, which empties nearby the cervix in women or the penis in men. the sphincter Inspiratory Muscle strength training around the urethral and the bladder work together to regulate urine flow in the bladder.
These are the functional unit of kidney.
- Regulating extracellular fluid volume The kidney is involved in helping to keep the plasma supply sufficient to maintain the essential organs’ blood flow.
- Changes in osmolarity.
- Maintaining ion concentrations in the proper range.
- Ensuring a stable pH.
- The excretion of poisons and wastes
- Hormone production.
Nephron:
How many nephrons are in each kidney?
The kidneys are made up of nephrons, which perform all of the functional units of the kidney. More than 20 million nephrons are present in each human kidney. The two areas of the human kidney where nephrons are found are the outer cortex and the inner medulla. The many parts of nephron. There are termed cortical nephrons when talking about the nephrons found in the cortex area. Contains juxtamedullary nephrons, medullary nephrons, or juxtamedullary nephrons may be found at the boundary between the cortex and the medulla.
Flowing urine takes on an important part in the process of concentrate manufacturing.
1 Bowman
2 Juxtamedullary nephron capsule is in the cortex.
Bowman’s capsule surrounds a cluster of capillaries called glomerulus in each nephron, while the inner end has a cup-shaped swelling, termed Bowman’s capsule.
The Nephrons’ Blood Supply
When blood travels via the afferent arterial system, it moves through the glomerulus, and as it moves through the glomerulus, it circulates blood in the capsule. A network of small blood vessels known as the glomerular capillaries branches to form a new network of larger vessels known as the common venous network. There are many capillaries (small blood vessels) that surround the left and right convoluted tubules.
After exiting the glomerulus, the filtrate goes through the several tubules inside the kidney, namely the renal pelvis, distal tubule, and finally, the tubule known as the urinary filter, which is used for making urine. distal and proximal tubules of the nephron intermingle with the peritubular capillaries. More capillaries are seen in juxtamedullary nephrons; they extend to form a loop of the vas recta artery.
- Cortical nephrons are free of venous refluxes
- Neuron-like nephrons
- It is made up of two components
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
The capsule after Boman’s tube goes on as an extremely convoluted tube known as the proximal convoluted tubule. At this point, things like fertilizer or nutrients are reabsorbed.
longitudinal and Radial Convoluted Tubules
Also termed the distal convoluted tubule, the last portion of the nephron is very convoluted. Here, the secretion of hydrogen atoms takes place to regulate the PH of urine.
The Loop of Henle
Nephron then makes a U-shaped bend, becoming rather narrow. The loop of Henle is also known as the loop of Henle.
- The Henle loop contains two sections
- A loop of Henle that descends
The loop of Henle when the filtrate goes downhill is the first loop in which that happens.
An upward spiral of the Henle
The portion of the loop of Henle in which the filtrate flows upward is known as the circulation chamber.
Tube Collecting
The collecting tubule receives filtrate from the distal tubule. The numerous collecting tubules are shared by many nephrons.
Function of Nephron
The two primary tasks of the kidney are to filter wastes and produce urine.
1 Development of urine
2 Osmoregulation
3 The development of urine
Urination may be categorized into three distinct stages.
1. Filtration
Filtered blood in the bowman’s capsule passes via the glomerulus is not as prominent elsewhere because glomerular walls are permeable. Because this percentage of blood pressure reached this location, this location contributes to the filtration pressure. Glomerular filtrate appears in the glomerulus. This fluid includes a lot of important compounds, including glucose, amino acids, and salts in water solution.
2. Reabsorption
In the proximal tubules, all the beneficial chemicals in the tubular fluid are reabsorbed. Once it exits the proximal tubule, the majority of nitrogenous wastes are found in the filtrate.
3. Secretion
Additionally, the tubular epithelium of the nephron releases chemicals into the lumen. This secretion is highly selective, and the majority of the secreted substance is primarily composed of hydrogen ions (H+ ions) to balance the PH level of the filtrate that passes through the tubule. Most of the time, the waste product infiltration is mostly urea, which is known as urine.
Which kidney does it affect more?
Due to the enormous size of the hepatic on the opposite side of the chest, the left kidney is positioned somewhat higher than the right kidney. The kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, therefore they are called retroperitoneal organs. Your kidneys help rid your body of waste and excess fluid. Also known as renal excretion, your kidneys get rid of the acid that is created by the body’s cells and keep your blood disorders lists in balance, including sodium, calcium, phosphate, and potassium.
To maintain your kidneys healthily, How can we do this?
- For those who want to maintain their kidneys healthy, here are some pointers.
- Exercise regularly and stay fit.
- Keep your blood sugar under control.
- Keep an eye on blood pressure.
- Avoid overeating and monitor weight.
- Drink a lot of water.
- It is very unhealthy to smoke.
- You should be mindful of the quantity of OTC medications you use.
- Testing your function of kidney is recommended if you have an increased risk of renal disease.
“medshelper.com, a health writing expert known around the world, was co-founded by Aneeza“